Introduction
Multimodal models are at the forefront of artificial intelligence (AI), enabling machines to interpret and interact with the world in ways that closely mimic human capabilities. These models are designed to process and integrate data from multiple sources, such as text, images, audio, and video, allowing them to perform complex tasks more efficiently and accurately. As AI continues to evolve, the importance of multimodal models in applications like virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and advanced analytics cannot be overstated. This article explores what multimodal models are, how they work, and their impact on various industries.
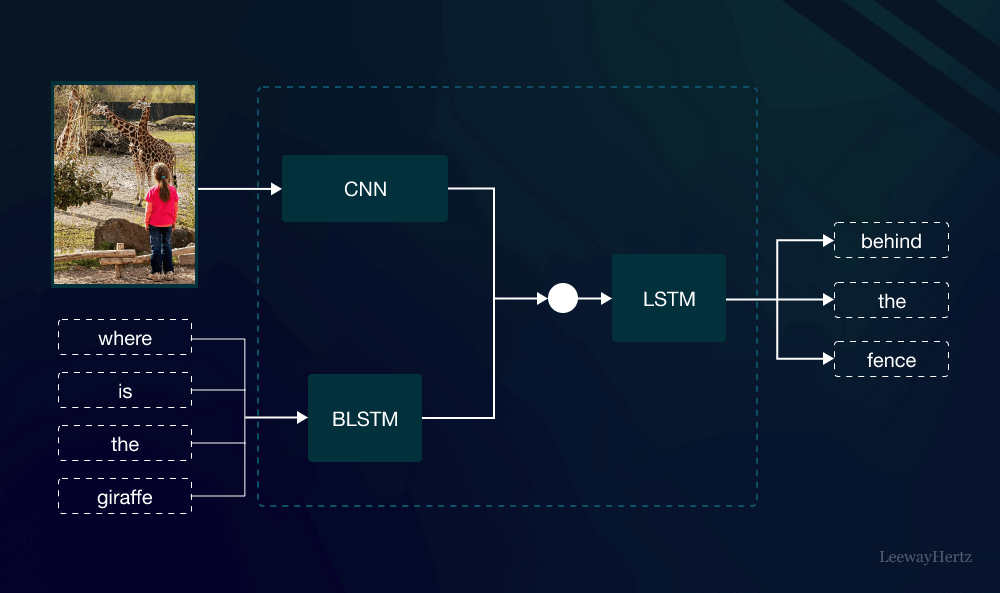
What Are Multimodal Models?
Multimodal models are AI systems capable of processing and understanding information from different modalities—such as visual, auditory, and textual data—simultaneously. Unlike traditional models that rely on a single type of input, multimodal models can combine information from multiple sources to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the data. For example, a multimodal model can analyze an image and its accompanying text to generate a more accurate description or make a more informed decision.
These models leverage advances in machine learning, particularly deep learning, to achieve high levels of performance across various tasks. By integrating data from diverse sources, multimodal models can recognize patterns, understand context, and generate responses that are more aligned with real-world complexities.
How Do Multimodal Models Work?
The functioning of multimodal models involves several key steps:
- Data Collection and Preprocessing: Multimodal models require large amounts of diverse data. This data is collected from various sources, such as images, videos, audio clips, and text documents. Preprocessing is then applied to clean and prepare the data, ensuring that it is suitable for training.
- Feature Extraction: In this stage, the model extracts relevant features from each modality. For instance, a model might use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image data and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or transformers for text data. These features capture essential characteristics that the model needs to understand the input.
- Data Fusion: The extracted features from different modalities are then combined or fused. This fusion can be done at various levels—early fusion integrates raw data, intermediate fusion combines extracted features, and late fusion merges the outputs of individual models. The goal is to create a unified representation that leverages the strengths of each modality.
- Model Training: Multimodal models are trained using labeled data, where the combined inputs are used to predict or classify outputs. Training involves adjusting the model’s parameters to minimize errors and improve accuracy. Techniques like backpropagation and gradient descent are commonly used in this phase.
- Prediction and Decision Making: Once trained, the multimodal model can make predictions or decisions based on new, unseen data. For example, in a medical diagnostic system, the model might analyze both medical images and patient records to diagnose a condition accurately.
Applications of Multimodal Models
Multimodal models have a wide range of applications across various fields:
- Healthcare: In healthcare, multimodal models can integrate data from medical images, patient histories, and genetic information to provide more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
- Autonomous Vehicles: These models are crucial in autonomous vehicles, where they combine data from cameras, lidar, radar, and other sensors to understand the driving environment and make safe decisions.
- Virtual Assistants: Multimodal models enhance virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa by allowing them to understand and respond to voice commands, recognize images, and even interpret emotions from user interactions.
- Content Generation: In creative industries, multimodal models are used to generate content, such as creating videos with synchronized audio and subtitles or generating text descriptions for images and videos.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their promise, multimodal models face several challenges:
- Data Integration: Combining data from different modalities can be complex due to varying data formats, noise levels, and alignment issues.
- Computational Resources: Multimodal models often require significant computational power and storage, which can be a barrier for some applications.
- Bias and Fairness: Ensuring that multimodal models are fair and unbiased is crucial, especially when they are used in sensitive areas like hiring or law enforcement.
Looking ahead, the future of multimodal models seems bright. Advances in AI research, improved algorithms, and more powerful hardware will likely address many of the current challenges. As these models become more sophisticated, they will play an increasingly important role in making AI systems more intelligent, adaptable, and capable of interacting with the world in a human-like manner.
Conclusion
Multimodal models represent a significant leap forward in the field of AI, offering the ability to process and understand data from multiple sources. This capability not only enhances the performance of AI systems but also opens up new possibilities in fields ranging from healthcare to entertainment. As we continue to refine and develop these models, they will undoubtedly become a cornerstone of future AI applications, making our interactions with technology more seamless and intuitive. Understanding and leveraging the power of multimodal models is key to unlocking the full potential of artificial intelligence.
Leave a comment