As the demand for customized language models grows, many organizations are exploring how to build a private LLM (Large Language Model) to meet specific needs. A private LLM provides enhanced data privacy, tailored functionalities, and the ability to operate in controlled environments. This article outlines the essential steps to build a private LLM, ensuring clarity and accessibility for readers of all backgrounds.
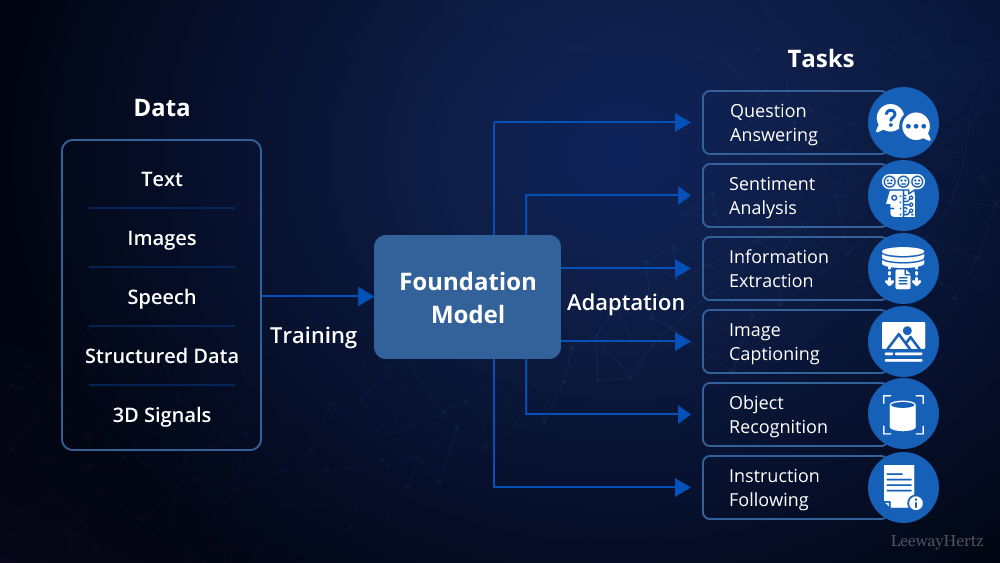
Understanding the Basics of LLMs
Before diving into the specifics of building a private LLM, it’s important to understand what LLMs are and how they function. LLMs are sophisticated AI models designed to understand and generate human language. They are trained on vast datasets, allowing them to perform various tasks, including text generation, summarization, translation, and more. By creating a private LLM, organizations can leverage this technology while maintaining control over their data and model behaviors.
Step 1: Define Your Objectives
The first step in the process of how to build a private LLM is to clearly define your objectives. Consider the following questions:
- What specific tasks do you want your LLM to perform?
- Who are the end users, and what are their needs?
- What level of customization is required?
Answering these questions will help shape the model’s design and functionalities. Whether your focus is on customer support, content creation, or data analysis, a well-defined purpose will guide the subsequent steps.
Step 2: Choose the Right Framework
Selecting an appropriate framework is crucial in the journey of how to build a private LLM. Numerous frameworks and libraries support LLM development, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Hugging Face Transformers. Consider the following factors when choosing a framework:
- Ease of Use: Opt for frameworks that provide clear documentation and community support.
- Scalability: Ensure the framework can handle large datasets and model complexities.
- Flexibility: Look for options that allow customization of models to suit your specific needs.
A well-chosen framework will simplify the development process and enhance the performance of your private LLM.
Step 3: Gather and Prepare Your Data
The quality and relevance of the data used to train your LLM are paramount. This step in how to build a private LLM involves collecting data that aligns with your defined objectives. Consider these key aspects:
- Data Sources: Identify reliable data sources, such as internal documents, databases, or publicly available datasets.
- Data Cleaning: Preprocess the data to eliminate errors, duplicates, and irrelevant information. This process may involve tokenization, normalization, and filtering.
- Data Annotations: For specific tasks, consider annotating your data to provide additional context that helps the model learn more effectively.
Investing time in data preparation will significantly enhance your model’s performance and relevance.
Step 4: Model Training
Training the LLM is a pivotal step in how to build a private LLM. This process involves several sub-steps:
- Model Selection: Choose a pre-existing model architecture that suits your objectives, such as GPT, BERT, or T5.
- Training Setup: Configure your training environment, including hardware resources (GPUs/TPUs), optimization algorithms, and hyperparameters.
- Training Process: Initiate the training process, which involves feeding your prepared data into the model. Monitor the training for performance metrics like loss and accuracy, and make adjustments as necessary.
Training a language model can be resource-intensive, so be prepared for the time and computational power required to achieve satisfactory results.
Step 5: Fine-Tuning and Optimization
Once your model has been trained, the next step in how to build a private LLM is fine-tuning and optimization. This stage focuses on improving the model’s performance and tailoring it to your specific use cases. Consider the following:
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Experiment with different hyperparameters, such as learning rate and batch size, to find the optimal settings for your model.
- Domain Adaptation: If your model will be used in a specific domain, consider fine-tuning it on domain-specific data to enhance its performance in that area.
- Evaluation: Use metrics such as perplexity, BLEU score, or F1 score to assess your model’s performance. Conduct qualitative evaluations by testing the model with real-world scenarios.
Fine-tuning is essential to ensure that your private LLM meets the desired performance standards.
Step 6: Deployment and Maintenance
After fine-tuning your model, the final step in how to build a private LLM is deployment and ongoing maintenance. This involves making the model accessible to end-users while ensuring it remains efficient and secure. Key considerations include:
- Deployment Environment: Choose a suitable environment for hosting your model, whether on-premises or in the cloud. Ensure that it meets the necessary security and compliance requirements.
- User Interface: Develop an interface that allows users to interact with the LLM seamlessly. This could involve APIs, web applications, or other integration methods.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the model’s performance and make necessary updates or retraining based on user feedback and changing data trends.
Proper deployment and maintenance will ensure that your private LLM remains relevant and effective over time.
Conclusion
Building a private LLM is a rewarding endeavor that requires careful planning, data preparation, and model optimization. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can successfully create a customized language model tailored to your specific needs. The journey of how to build a private LLM may be complex, but the benefits of enhanced privacy, control, and customization make it worthwhile. Whether for business applications, research, or personal projects, a private LLM can significantly enhance your ability to leverage the power of language understanding and generation.
Leave a comment