Building your own private Language Model (LLM) can offer significant advantages, especially for businesses and individuals who need enhanced data privacy, customization, and control over their artificial intelligence capabilities. This guide will walk you through the essential steps on how to build a private LLM, explaining the core requirements and best practices to ensure your project is a success.
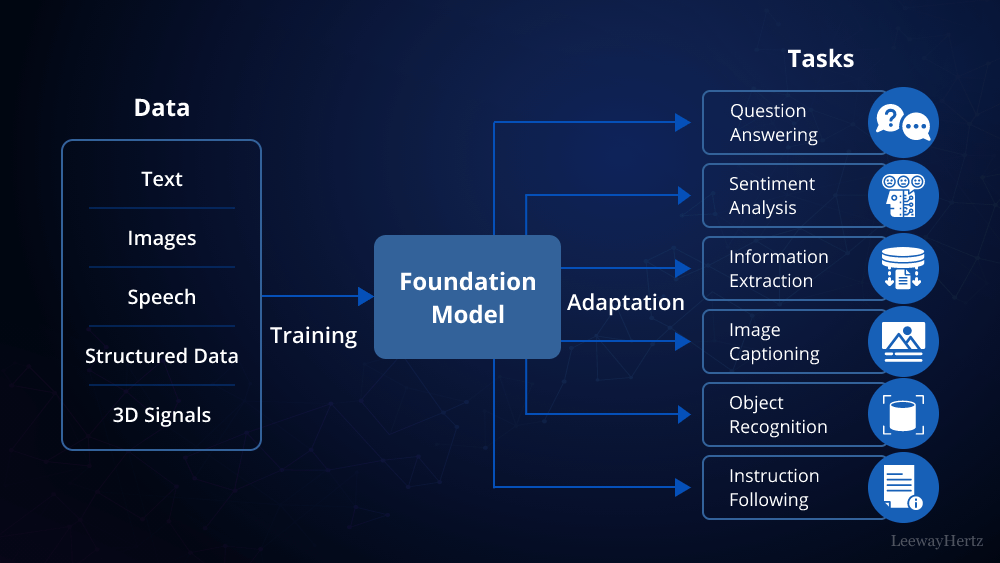
1. Understanding What an LLM Is
Before diving into how to build a private LLM, it’s crucial to understand what an LLM is. A Language Model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence designed to understand and generate human-like text. Popular examples include OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Google’s BERT. These models are trained on massive datasets and can perform various tasks, such as text completion, summarization, translation, and more.
However, public LLMs often come with limitations in terms of data privacy and customization. This is where building a private LLM becomes beneficial.
2. Why Build a Private LLM?
There are several reasons why you might want to build a private LLM:
- Data Privacy: Sensitive data remains within your control, reducing the risk of exposure.
- Customization: Tailor the model to specific tasks, industries, or company requirements.
- Cost Efficiency: Over time, a private LLM can be more cost-effective than relying on third-party services.
3. Key Steps to Build a Private LLM
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Use Cases
Start by clearly defining the goals and specific use cases for your private LLM. Are you looking to automate customer service, generate content, or develop a chatbot? Understanding the primary function of your model will help you determine the right architecture, dataset, and scale for your project.
Step 2: Choose the Right Model Architecture
The architecture of your LLM is crucial and will depend on your specific needs. Common architectures include:
- Transformer Models: Such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) or BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
- RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks): Good for sequential data but less popular than Transformers for LLMs.
- Custom Architectures: Tailored to specific tasks or industries.
Selecting an appropriate architecture is essential when learning how to build a private LLM, as it will determine your model’s capabilities and performance.
Step 3: Prepare the Dataset
A high-quality dataset is the backbone of any LLM. Your dataset should be extensive and relevant to your LLM’s intended use. For a private LLM, consider using proprietary data, public datasets, or a combination of both. Ensure that the data is clean, well-annotated, and free from biases that could affect the model’s performance.
Step 4: Set Up Your Infrastructure
Building an LLM requires significant computational resources. You’ll need:
- Cloud Services: AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure provide scalable computing resources.
- On-Premises Servers: For greater control and security, though this option can be more expensive and complex to manage.
- High-Performance GPUs: Essential for training large models.
When setting up your infrastructure, consider the trade-offs between cost, control, and scalability.
Step 5: Train Your Model
Training is the most resource-intensive step in building a private LLM. It involves feeding the dataset into the model and allowing it to learn patterns and relationships in the data. The training process can take days or even weeks, depending on the model size and complexity. Ensure you monitor the training process closely, adjusting parameters as needed to improve accuracy and performance.
Step 6: Evaluate and Fine-Tune
Once your LLM is trained, it’s essential to evaluate its performance. Use validation datasets to test the model’s accuracy and adjust parameters or retrain as necessary. Fine-tuning involves tweaking the model to better fit specific tasks, which is a crucial step in the process of how to build a private LLM.
Step 7: Deploy and Monitor
After your private LLM is trained and fine-tuned, the next step is deployment. You can deploy it on a private server, cloud platform, or integrate it into your existing applications. Continuous monitoring is crucial to ensure the model remains accurate and performs as expected. Regular updates and retraining with new data can help maintain its effectiveness over time.
4. Best Practices for Building a Private LLM
- Data Security: Implement strong security measures to protect your data during training and deployment.
- Compliance: Ensure your LLM complies with relevant data protection laws and regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
- Scalability: Design your LLM with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth or additional use cases.
5. Challenges to Consider
Building a private LLM is not without challenges. It requires significant investment in resources, expertise, and ongoing maintenance. Additionally, ensuring data quality and model accuracy can be complex and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Learning how to build a private LLM can unlock numerous benefits, from improved data privacy to customized AI solutions tailored to your specific needs. By following these steps and best practices, you can develop a powerful LLM that aligns with your goals and provides a competitive advantage in your field. While the process may seem daunting, the rewards of a tailored, private LLM can far outweigh the challenges.
Leave a comment