Artificial intelligence (AI) has made remarkable strides in recent years, transforming industries and reshaping the way we interact with technology. However, traditional AI models often struggle with understanding the cause-and-effect relationships inherent in complex data. This is where Causal AI steps in, offering a more nuanced approach to AI that goes beyond mere correlation. In this article, we will explore what Causal AI is, its significance, how it works, and its potential applications across various sectors.
What is Causal AI?
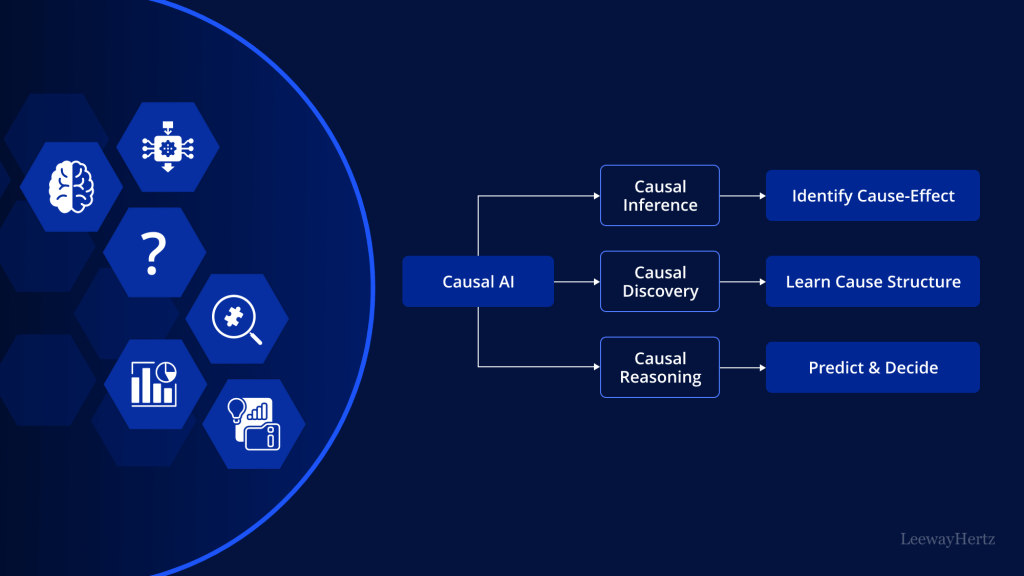
Causal AI, or Causal Artificial Intelligence, is a branch of AI that focuses on identifying and understanding causal relationships within data. Unlike traditional AI models that primarily rely on correlations, Causal AI seeks to determine the cause-and-effect dynamics that drive outcomes. This ability to differentiate between correlation and causation allows Causal AI to make more accurate predictions, provide better insights, and support decision-making processes that are rooted in the true nature of the data.
Traditional AI models, such as machine learning algorithms, can identify patterns and associations within data but often fail to explain why these patterns exist. Causal AI, on the other hand, uses causal inference techniques to establish a direct connection between variables, enabling it to predict the impact of changes more effectively. This approach makes Causal AI particularly valuable in scenarios where understanding the underlying mechanisms is crucial, such as healthcare, finance, and policy-making.
How Does Causal AI Work?
Causal AI relies on a combination of data science, statistics, and domain knowledge to identify causal relationships. The core of Causal AI is built around causal graphs, which are graphical representations of the relationships between variables. These graphs help in visualizing and analyzing the causal structure of data, making it easier to identify which factors are driving outcomes and which are merely associated with them.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how Causal AI works:
- Data Collection and Preparation: The process begins with gathering and cleaning data, ensuring it is suitable for analysis. This step is similar to traditional AI but with a focus on variables that are likely to have causal connections.
- Causal Discovery: Causal discovery involves identifying potential causal relationships between variables. Techniques such as randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and statistical algorithms are used to explore these relationships.
- Causal Inference: Once potential causal links are identified, causal inference techniques are applied to estimate the strength and direction of these relationships. This step often involves advanced statistical methods, such as Bayesian networks or structural equation modeling, to confirm causality.
- Validation and Testing: The identified causal models are validated using real-world data or simulations to ensure their accuracy. This step helps in refining the models and improving their predictive power.
- Deployment and Application: Finally, the causal models are deployed in applications where understanding cause-and-effect is crucial. This could range from predicting patient outcomes in healthcare to optimizing marketing strategies in business.
Applications of Causal AI
Causal AI has a wide range of applications across various industries, thanks to its ability to provide deeper insights and more reliable predictions. Here are some key areas where Causal AI is making a significant impact:
1. Healthcare:
In healthcare, understanding causal relationships can be critical for diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and developing treatment plans. Causal AI can help identify the true causes of health conditions, leading to more effective interventions and personalized care. For instance, it can distinguish between symptoms that are directly caused by a disease and those that are side effects of medication.
2. Finance:
In the finance sector, Causal AI can be used to model economic trends, assess the impact of policy changes, and improve risk management. By understanding the causal factors behind market movements, financial institutions can make more informed decisions, reducing uncertainty and improving investment strategies.
3. Marketing:
Marketers can leverage Causal AI to optimize campaigns by understanding which factors truly drive consumer behavior. This can lead to more effective targeting and resource allocation, as it identifies the causal drivers of customer actions rather than just correlations.
4. Public Policy:
Causal AI can play a crucial role in public policy by helping policymakers understand the effects of their decisions. For example, it can be used to assess the impact of new regulations, social programs, or economic policies, ensuring that interventions are based on solid causal evidence rather than assumptions.
The Future of Causal AI
The future of Causal AI looks promising, as it continues to evolve and expand its capabilities. With advancements in computational power, data availability, and methodological innovations, Causal AI is poised to become an integral part of AI development. As industries increasingly recognize the limitations of correlation-based models, the demand for Causal AI is expected to grow, driving further research and applications.
In conclusion, Causal AI represents a significant leap forward in the field of artificial intelligence. By focusing on cause-and-effect relationships, it offers a more robust framework for understanding complex data, making it a powerful tool for decision-making in various domains. As Causal AI continues to mature, its potential to transform industries and improve outcomes will only increase, making it an exciting area to watch in the coming years.
Leave a comment