Multi-agent systems (MAS) are gaining popularity in artificial intelligence and computer science due to their ability to solve complex problems. These systems consist of multiple autonomous agents that work together to achieve specific goals. In this article, we will explore the types, working principles, applications, and benefits of multi-agent systems. Understanding these aspects will help you grasp how MAS can revolutionize various industries.
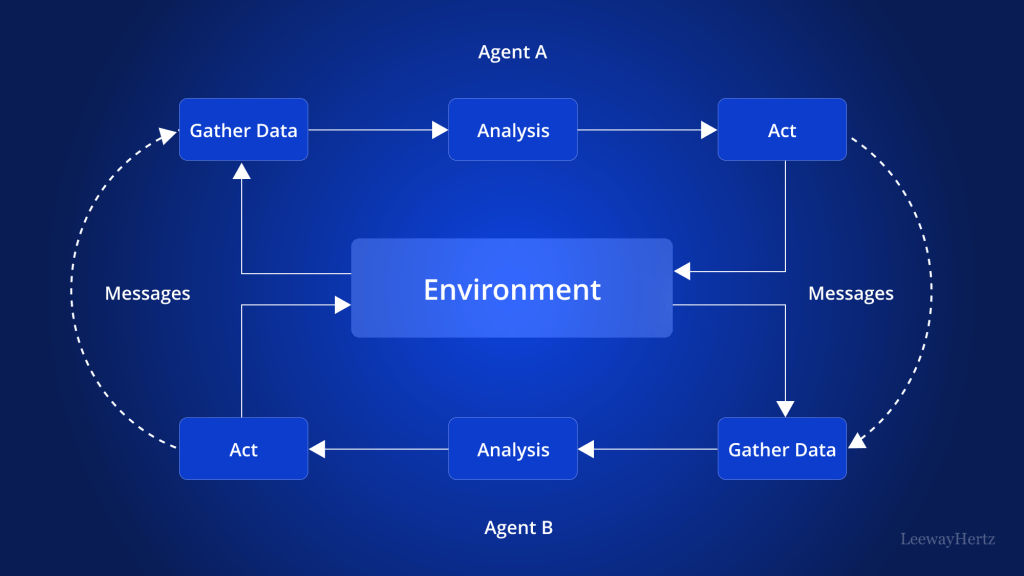
What is a Multi-Agent System?
A multi-agent system is a computational system that consists of multiple interacting agents. Each agent is an independent entity capable of making decisions, learning, and interacting with other agents to perform tasks. The agents can be software programs, robots, or any other autonomous entities that operate within an environment. The collaborative and distributed nature of multi-agent systems allows them to handle complex problems that are difficult for a single agent to solve.
Types of Multi-Agent Systems
There are several types of multi-agent systems, each designed to meet specific requirements and challenges. The main types include:
- Cooperative Multi-Agent Systems
In cooperative multi-agent systems, all agents work together towards a common goal. They share information, coordinate actions, and optimize their strategies collectively. These systems are commonly used in collaborative tasks, such as disaster response, resource management, and team-based games. - Competitive Multi-Agent Systems
In competitive multi-agent systems, agents have conflicting goals and compete against each other. These systems are often seen in scenarios like market simulations, where agents represent competing companies or bidders. The goal of each agent is to maximize its own benefits, which may be at the expense of others. - Hybrid Multi-Agent Systems
Hybrid multi-agent systems combine both cooperative and competitive behaviors. Agents may collaborate in certain aspects while competing in others. This type is useful in complex environments where multiple goals and constraints exist, such as supply chain management, where companies may cooperate for logistics but compete for market share. - Homogeneous Multi-Agent Systems
In homogeneous multi-agent systems, all agents are identical in terms of capabilities and objectives. These systems are often used in scenarios where uniformity and scalability are required, such as sensor networks or distributed computing. - Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems
Heterogeneous multi-agent systems consist of agents with different abilities, roles, and goals. This type is particularly suited for tasks that require diverse skill sets, such as autonomous vehicles working with drones for surveillance.
How Multi-Agent Systems Work
Multi-agent systems function based on a few key principles:
- Agent Autonomy
Each agent in a multi-agent system operates independently, making decisions based on its perception of the environment and its goals. Autonomy allows agents to adapt to changes and make real-time decisions without centralized control. - Interaction and Communication
Agents communicate with each other to share information, coordinate actions, and negotiate solutions. This interaction is crucial for the overall functioning of the system, as it enables agents to work together efficiently. - Distributed Problem Solving
In a multi-agent system, problem-solving is distributed among agents. Each agent is responsible for a portion of the task, and they work collaboratively to achieve the overall goal. This distributed approach enhances the system’s scalability and robustness. - Learning and Adaptation
Many multi-agent systems incorporate learning mechanisms, allowing agents to improve their performance over time. Through techniques like machine learning and reinforcement learning, agents can adapt their strategies based on past experiences.
Applications of Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems are widely used in various fields, offering innovative solutions to complex problems. Some key applications include:
- Robotics and Automation
Multi-agent systems are employed in robotics for coordinated tasks, such as warehouse automation, drone fleets, and robotic swarms. They enhance efficiency and flexibility in performing complex, multi-step processes. - Smart Grids and Energy Management
In smart grids, multi-agent systems help optimize energy distribution, load balancing, and fault management. Agents can represent different components of the grid, such as generators, consumers, and storage units, working together to maintain stability. - Traffic and Transportation Management
Multi-agent systems are used in traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve routing. Each agent can represent a vehicle, making autonomous decisions based on traffic conditions and other agents’ actions. - Finance and Market Simulation
In finance, multi-agent systems are used for market simulations, trading algorithms, and predictive analysis. Agents can simulate the behavior of market participants, helping in risk assessment and strategy development. - Healthcare and Medical Diagnosis
Multi-agent systems are utilized in healthcare for patient monitoring, diagnostic support, and personalized treatment plans. Agents can collaborate to analyze data from various sources, offering more accurate and timely interventions.
Benefits of Multi-Agent Systems
The adoption of multi-agent systems offers several advantages:
- Scalability
Multi-agent systems can easily scale by adding more agents, making them suitable for large-scale applications without significant performance degradation. - Flexibility and Adaptability
Agents in a multi-agent system can adapt to dynamic environments, making the system robust to changes and uncertainties. - Enhanced Problem-Solving Capabilities
By distributing tasks among multiple agents, multi-agent systems can tackle complex problems more efficiently than centralized systems. - Cost-Effectiveness
The distributed nature of multi-agent systems reduces the need for centralized infrastructure, leading to lower operational costs and increased efficiency. - Improved Decision-Making
Multi-agent systems enable more informed decision-making by leveraging collective intelligence, leading to better outcomes in various applications.
Conclusion
Multi-agent systems represent a powerful approach to solving complex problems through the collaboration of autonomous agents. Understanding the types, working mechanisms, applications, and benefits of these systems highlights their potential to transform industries. As technology advances, the role of multi-agent systems will continue to grow, driving innovation and efficiency across multiple domains.
Leave a comment