Generative AI is transforming various industries by enabling machines to create text, images, music, and even code. However, to harness the full potential of generative models, it is often necessary to fine-tune a pre-trained model. Fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications can significantly enhance performance and adapt the model to specific tasks or datasets. In this article, we will guide you through the process of fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications.
1. Understanding the Importance of Fine-Tuning
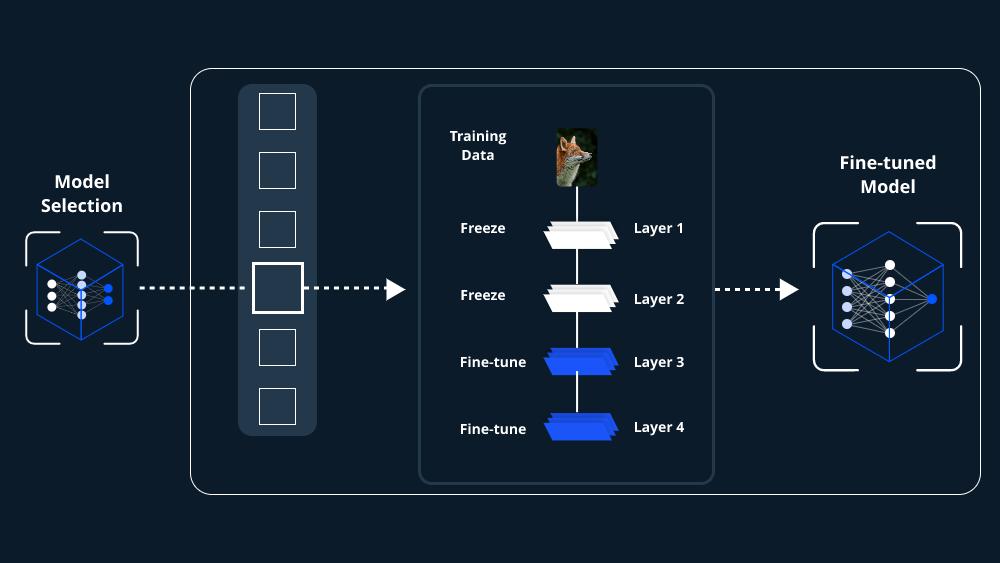
Fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications involves taking a model that has already been trained on a large dataset and refining it further on a specific, often smaller, dataset. This process helps the model to adapt to new tasks or domains while retaining the knowledge it has acquired during its initial training.
Why Fine-Tuning is Necessary
Pre-trained models are often trained on general datasets, which means they have a broad understanding of various topics. However, generative AI applications may require the model to generate content within a specific niche, style, or format. Fine-tuning allows the model to specialize in these areas, improving its accuracy and relevance for the intended application.
2. Preparing for Fine-Tuning
Before you can fine-tune a pre-trained model for generative AI applications, several preparatory steps are essential. These include selecting the right pre-trained model, preparing your dataset, and setting up your computational environment.
Choosing the Right Pre-Trained Model
The first step in fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications is selecting a model that aligns closely with your desired output. Popular pre-trained models include GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) for text generation, StyleGAN for image generation, and others. Your choice will depend on the type of content you wish to generate.
Dataset Preparation
The dataset you use for fine-tuning should be carefully curated to match the specific requirements of your generative AI application. For example, if you are fine-tuning a text generation model to create poetry, your dataset should consist of poems, rather than general text. The quality and relevance of your dataset directly impact the effectiveness of the fine-tuning process.
Setting Up the Environment
Fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications often requires significant computational resources. Ensure that you have access to a powerful GPU or cloud-based computing platform. Additionally, you will need software libraries such as TensorFlow or PyTorch, along with the necessary dependencies.
3. The Fine-Tuning Process
Once your preparations are complete, you can begin the process of fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications. This involves several key steps, from data preprocessing to model training.
Data Preprocessing
Before feeding your dataset into the model, it’s important to preprocess it. This may involve tokenizing text data, resizing images, or normalizing values. The goal is to ensure that the data is in a format that the pre-trained model can process effectively.
Adjusting Model Parameters
When fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications, you may need to adjust certain model parameters. These include the learning rate, batch size, and the number of epochs. The learning rate determines how quickly the model adapts to new data, while the batch size and number of epochs control how many data samples the model processes at a time and how many times it cycles through the entire dataset, respectively.
Training the Model
With your data preprocessed and parameters set, you can begin the fine-tuning process. This involves training the model on your specific dataset while monitoring its performance. During training, the model’s weights are adjusted based on the new data, helping it to generate more accurate and relevant content for your application.
Monitoring and Evaluation
As you fine-tune a pre-trained model for generative AI applications, it’s crucial to monitor its performance. Use validation datasets to assess the model’s accuracy and adjust parameters if necessary. Overfitting, where the model performs well on the training data but poorly on new data, is a common issue that can be mitigated by techniques such as dropout or early stopping.
4. Post Fine-Tuning Steps
After you have successfully fine-tuned your pre-trained model, there are additional steps to take before deploying it in a generative AI application.
Model Evaluation
Evaluate the fine-tuned model thoroughly to ensure it meets your application’s requirements. This evaluation should include both quantitative metrics (like accuracy) and qualitative assessments (such as the coherence or creativity of the generated content).
Hyperparameter Optimization
To further improve the model’s performance, consider hyperparameter optimization. This process involves systematically adjusting the model’s hyperparameters to find the optimal settings for your specific task.
Deployment
Once the model has been fine-tuned and evaluated, it’s ready for deployment. Depending on your application, deployment may involve integrating the model into a web application, mobile app, or other software platform.
5. Conclusion
Fine-tuning a pre-trained model for generative AI applications is a powerful technique that enables the creation of highly specialized and effective AI systems. By following the steps outlined in this guide—selecting the right model, preparing your dataset, adjusting parameters, and carefully monitoring the fine-tuning process—you can optimize your generative AI models for a wide range of applications. Whether you’re working on text generation, image creation, or any other generative AI task, fine-tuning will help you achieve better, more tailored results.
Leave a comment