Building a private Language Model (LLM) can be a valuable asset for businesses and developers looking to leverage the power of AI while maintaining control over their data and intellectual property. This article will walk you through the key steps involved in creating your own private LLM.
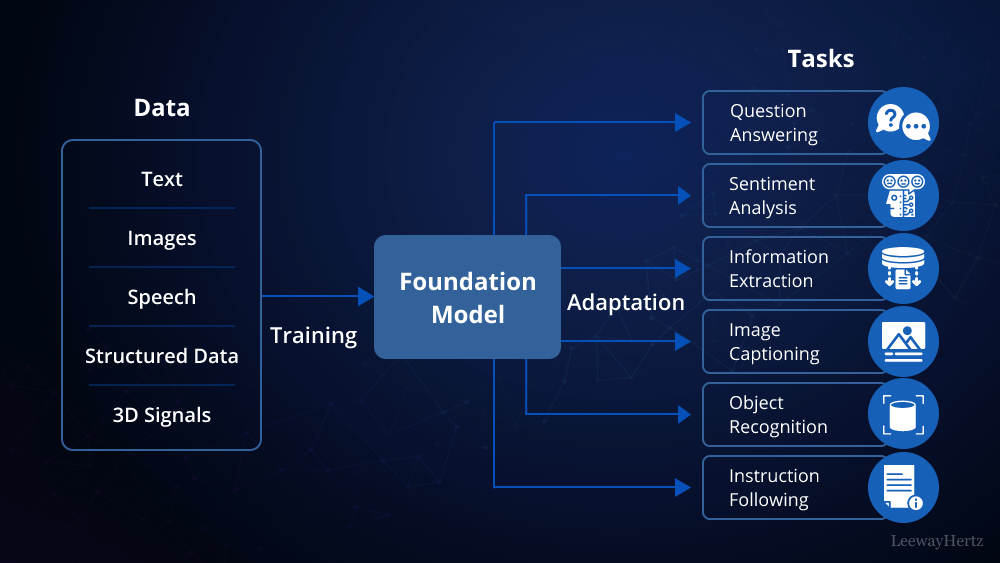
Introduction to Private LLMs
Language models have revolutionized natural language processing, enabling applications ranging from chatbots to advanced text analysis. While public models like OpenAI’s GPT-4 are powerful, they might not suit all needs due to privacy concerns, data sensitivity, or specific customization requirements. Building a private LLM addresses these issues by allowing you to train and deploy a model tailored to your needs, securely within your own infrastructure.
Understanding the Basics
1. What is a Language Model?
A language model is an AI system designed to understand and generate human language. It predicts the next word in a sentence, enabling it to complete text, answer questions, and perform other language-related tasks.
2. Why Build a Private LLM?
- Data Privacy: Maintain full control over your data.
- Customization: Tailor the model to specific industry or organizational needs.
- Performance: Optimize the model for your unique applications.
- Cost: Long-term savings on subscription fees for third-party services.
Key Steps to Building a Private LLM
1. Define Your Objectives
Before starting, clearly define what you want your LLM to achieve. This includes the type of text it will generate, the specific tasks it will perform, and the domain it will operate in. Having a clear goal will guide your decisions throughout the process.
2. Gather and Prepare Data
The quality of your language model depends heavily on the data it is trained on. Follow these steps to prepare your data:
- Data Collection: Gather a large corpus of text relevant to your domain. This can include books, articles, emails, or any other textual data.
- Data Cleaning: Remove any irrelevant or sensitive information. Clean data ensures better model performance and avoids potential biases.
- Data Preprocessing: Tokenize the text, convert it to a format suitable for training, and split it into training, validation, and test sets.
3. Choose the Right Framework and Tools
Selecting the appropriate framework is crucial for building and training your LLM. Some popular frameworks include:
- TensorFlow: A versatile and widely-used deep learning framework.
- PyTorch: Known for its flexibility and ease of use, particularly for research and development.
- Hugging Face Transformers: A library providing state-of-the-art pre-trained models and tools for natural language processing.
4. Design the Model Architecture
Designing the architecture of your language model involves deciding on the number of layers, the size of the hidden units, and other hyperparameters. You can start with a pre-trained model and fine-tune it to your specific needs or build a model from scratch if you have sufficient data and computational resources.
5. Train Your Model
Training an LLM is computationally intensive and requires significant resources. Consider the following:
- Hardware: Use GPUs or TPUs for faster training times.
- Training Duration: Depending on your data size and model complexity, training can take from a few hours to several weeks.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor the training process to adjust hyperparameters and ensure the model is learning effectively.
6. Evaluate and Fine-Tune
Once your model is trained, evaluate its performance using the validation and test sets. Key metrics to consider include accuracy, perplexity, and F1 score. Fine-tune the model based on these evaluations to improve its performance.
7. Deploy Your Model
Deploying your LLM involves setting up an environment where it can be accessed and used by applications. This might include:
- APIs: Create APIs to integrate your model with other systems.
- Server Infrastructure: Ensure your servers can handle the computational load.
- Security Measures: Implement security protocols to protect your model and data.
8. Maintain and Update
Maintaining your LLM is an ongoing process. Regularly update it with new data, retrain it to improve performance, and monitor its usage to detect and address any issues that arise.
Challenges and Considerations
Building a private LLM comes with several challenges:
- Data Privacy: Ensure that your data collection and usage comply with legal and ethical standards.
- Resource Intensive: Be prepared for the significant computational and financial resources required.
- Technical Expertise: Developing and maintaining an LLM requires advanced knowledge in machine learning and natural language processing.
Conclusion
Creating a private LLM offers numerous benefits, from enhanced data privacy to customized performance. By following these steps—defining objectives, gathering and preparing data, choosing the right tools, designing the model, training, evaluating, deploying, and maintaining—you can build a robust and efficient language model tailored to your specific needs. Embrace the power of private LLMs to unlock new possibilities for your business or projects.
Leave a comment