Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI), the efficiency and adaptability of models are crucial factors. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) emerges as a groundbreaking technique designed to optimize AI models for diverse tasks without excessive computational costs. This article explores the concept of PEFT, its significance, and its implications for the future of AI applications.
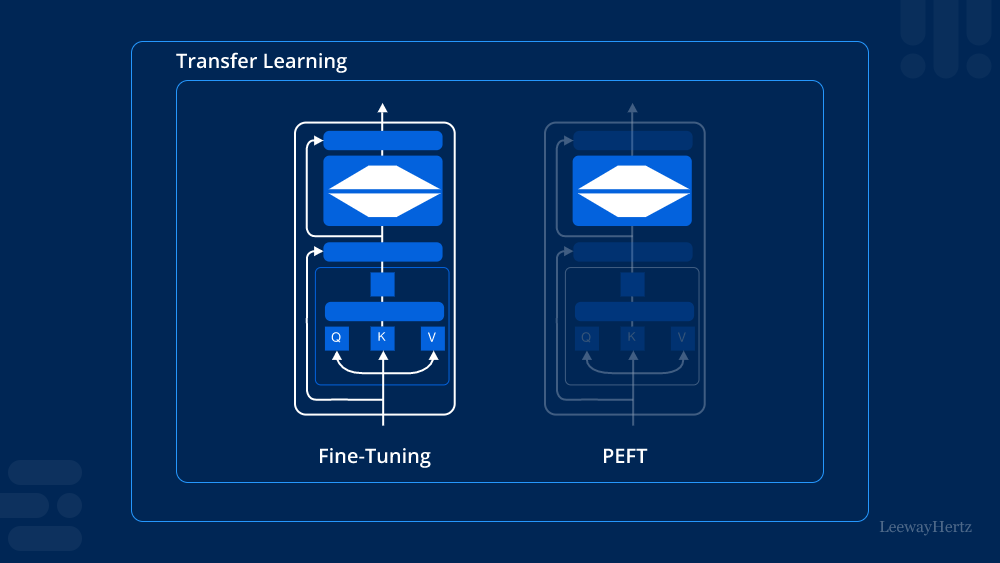
Understanding Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT)
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is a methodology within machine learning that aims to enhance the performance of pre-trained AI models through targeted adjustments of their parameters. Unlike traditional fine-tuning approaches that often require extensive computational resources and large-scale datasets, PEFT focuses on maximizing efficiency without compromising on accuracy.
How PEFT Works
PEFT leverages the knowledge encoded in pre-trained models, such as BERT or GPT, which have been trained on vast amounts of data to understand language, images, or other domains. Instead of starting from scratch for each new task, PEFT fine-tunes these models by selectively adjusting their parameters using a smaller, task-specific dataset. This targeted adjustment process refines the model’s understanding and improves its performance on specific tasks, making it more adaptable and resource-efficient.
Benefits of PEFT
- Computational Efficiency: By building upon pre-existing knowledge, PEFT reduces the need for extensive computational resources and training time, making AI applications more accessible and cost-effective.
- Versatility: PEFT enables AI models to quickly adapt to new tasks or domains with minimal additional training, enhancing their versatility and applicability across various industries and applications.
- Performance Optimization: Through fine-tuning, PEFT enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of AI models on specific tasks, achieving competitive performance benchmarks with significantly fewer resources.
Applications of PEFT
PEFT has profound implications across numerous fields and applications:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enhancing language understanding models like BERT for sentiment analysis, translation tasks, or text classification.
- Computer Vision: Optimizing image recognition models such as ResNet for object detection, scene understanding, or medical imaging analysis.
- Recommendation Systems: Improving recommendation algorithms by fine-tuning models to better understand user preferences and behavior patterns.
Future Directions
The future of PEFT lies in its continued evolution and integration into broader AI frameworks:
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining PEFT with other techniques such as transfer learning and meta-learning to further enhance model adaptability and efficiency.
- Automated Fine-tuning: Developing automated methods to streamline the PEFT process, reducing the need for manual intervention and accelerating deployment.
- Interdisciplinary Applications: Extending PEFT beyond traditional domains into healthcare, finance, and social sciences to address complex real-world challenges.
Conclusion
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) represents a pivotal advancement in AI research and applications, offering a balanced approach to enhancing model performance while optimizing computational resources. By leveraging pre-existing knowledge and targeted adjustments, PEFT not only improves efficiency but also expands the scope of AI applications across diverse industries. As researchers and practitioners continue to refine and innovate within this framework, the potential for PEFT to revolutionize how AI models are developed and deployed remains profound.
Leave a comment