Introduction
In the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), generative AI stands out as a transformative technology that pushes the boundaries of what machines can create. At its core, the generative AI tech stack encompasses a sophisticated set of tools and frameworks designed to enable machines to generate content, mimic human creativity, and enhance various industries from art to healthcare.
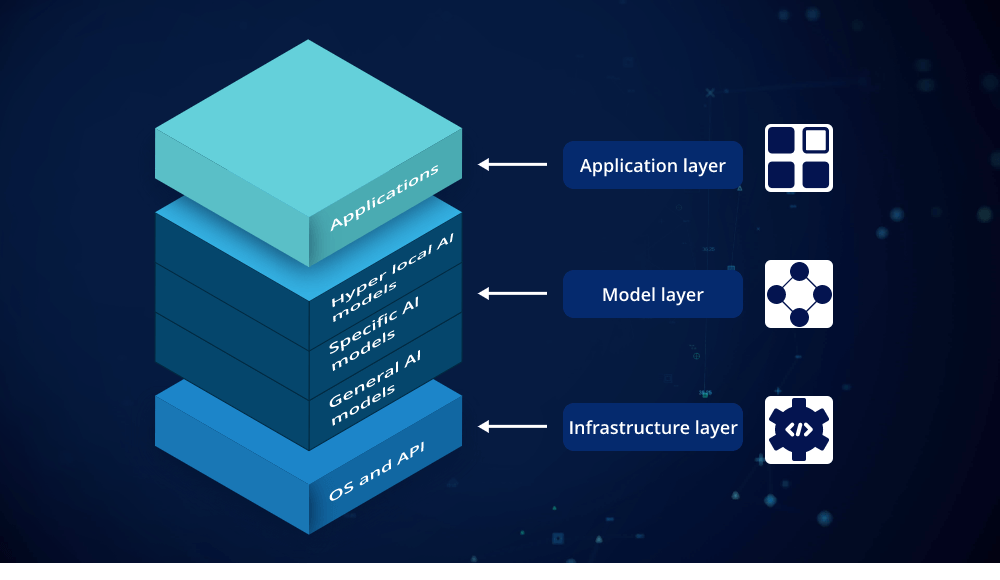
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI refers to a subset of AI technologies that focus on creating new content rather than simply interpreting data or making decisions based on predefined rules. Unlike traditional AI models that rely on large datasets for pattern recognition, generative AI leverages techniques such as neural networks to generate new data based on the patterns it has learned. This ability to create new content autonomously is what sets generative AI apart and makes it a powerful tool for innovation.
Components of the Generative AI Tech Stack
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning Central to the generative AI tech stack are neural networks, particularly deep learning models. These networks are structured to simulate the human brain’s interconnected neurons, enabling them to process vast amounts of data and learn intricate patterns. In generative AI, deep learning models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are commonly used to generate realistic images, videos, text, and even music.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Models Within the realm of text and language, NLP models like OpenAI’s GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) have revolutionized content generation. These models are trained on large datasets and can generate human-like text, translate languages, summarize documents, and even engage in conversation. NLP models are a critical component of the generative AI tech stack, enabling applications in automated content creation, customer service, and more.
- Computer Vision Algorithms Computer vision plays a crucial role in generative AI applications that involve visual content. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are at the forefront, enabling machines to interpret and generate images and videos. Style transfer algorithms, for example, allow artists and designers to apply the characteristics of one image to another, fostering new creative possibilities in digital art and design.
- Reinforcement Learning Reinforcement learning provides a framework for training AI agents to make sequential decisions in dynamic environments. While not exclusive to generative AI, reinforcement learning techniques are integrated into the tech stack to improve the autonomy and decision-making capabilities of generative systems. This is particularly useful in applications like game playing, robotics, and personalized content recommendation systems.
Applications Across Industries
Generative AI has far-reaching implications across various industries, transforming how businesses operate and innovate:
- Art and Design: Artists use generative AI tools to explore new creative styles and automate repetitive tasks like colorization or pattern generation.
- Healthcare: In medicine, generative AI assists in medical imaging analysis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment recommendations based on patient data.
- Entertainment: Film studios and game developers employ generative AI for creating realistic CGI, immersive virtual worlds, and adaptive storytelling experiences.
- Marketing and Content Creation: Generative AI powers personalized marketing campaigns, content recommendation engines, and automated writing assistants that generate SEO-friendly articles.
- Education: AI-driven tutoring systems adapt to individual learning styles, providing personalized feedback and resources to students.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the generative AI tech stack holds immense promise, several challenges must be addressed:
- Ethical Concerns: Issues surrounding AI bias, privacy, and the ethical implications of AI-generated content require careful consideration.
- Complexity and Interpretability: Deep learning models can be opaque, making it challenging to understand how and why they generate specific outputs.
- Data Quality and Availability: Generative models require large datasets for training, raising concerns about data privacy and accessibility.
Looking ahead, advancements in generative AI are likely to focus on enhancing model interpretability, improving data efficiency, and addressing ethical concerns to foster responsible AI development.
Conclusion
The generative AI tech stack represents a monumental leap in AI capabilities, empowering machines to create, innovate, and augment human creativity across diverse domains. As research and development continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the transformative potential of generative AI promises to reshape industries, drive innovation, and inspire new modes of expression in the digital age.
Leave a comment